Over the past few years, discussions about the changing climate have become heated. While there are numerous varying theories on how the rise of the earth’s temperature will affect us in the future, there are many ways we are experiencing the effects today. With extraordinary high and low temperatures being recorded around the world, many people are wondering what’s causing these drastic swings in temperature. From blistering heat waves to freezing cold temperatures, let’s look into how the rise in temperature is impacting weather conditions today.
 2019 showed us some temperature extremes that we’ve never seen before
2019 showed us some temperature extremes that we’ve never seen before
Record Heat
As you may have seen in various reports, July 2019 was the warmest month on record for the global average temperature according to organizations like the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Programme and the US National Ocean and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). 9 out the 10 warmest Julys on record have also occurred after the year 2005. The NOAA has also reported that 2019 is on course to tie for the second warmest year on record only behind 2016, which is the warmest year recorded so far. With the global average temperature on the rise, the impact of this change is creating an unusual temperature phenomenon in places around the world.
Monitor the current global temperature in real time!
Erratic Hot and Cold
How are these changes in temperature affecting us around the world? France, Belgium and the Netherlands recorded record high temperatures this summer with Paris soaring to 42°C (109°F). Chicago also endured a record low daily temperature of -30°C (-23°F) in January of this year with wind chill between -42°C and -48°C (-45°F and -55°F). These extreme lows caused schools to close and even public services to be suspended. Sensors on the Greenland ice cap, which is located 3,200m above sea level and houses ice below over a mile think, also recorded a temperature of 3.2°C. This is the highest temperature ever recorded as the temperature there rarely creeps above zero degrees. However, the temperature in the atmosphere is not the only factor changing. Average ocean temperatures are also rising according to the ‘Advances in Atmospheric Sciences’ report issued in January of 2019. These new observations indicate that 2018 was the warmest year for global ocean temperatures with the highest heat content since the 1950s. We are certainly experiencing new record temperatures and feeling it around the world.
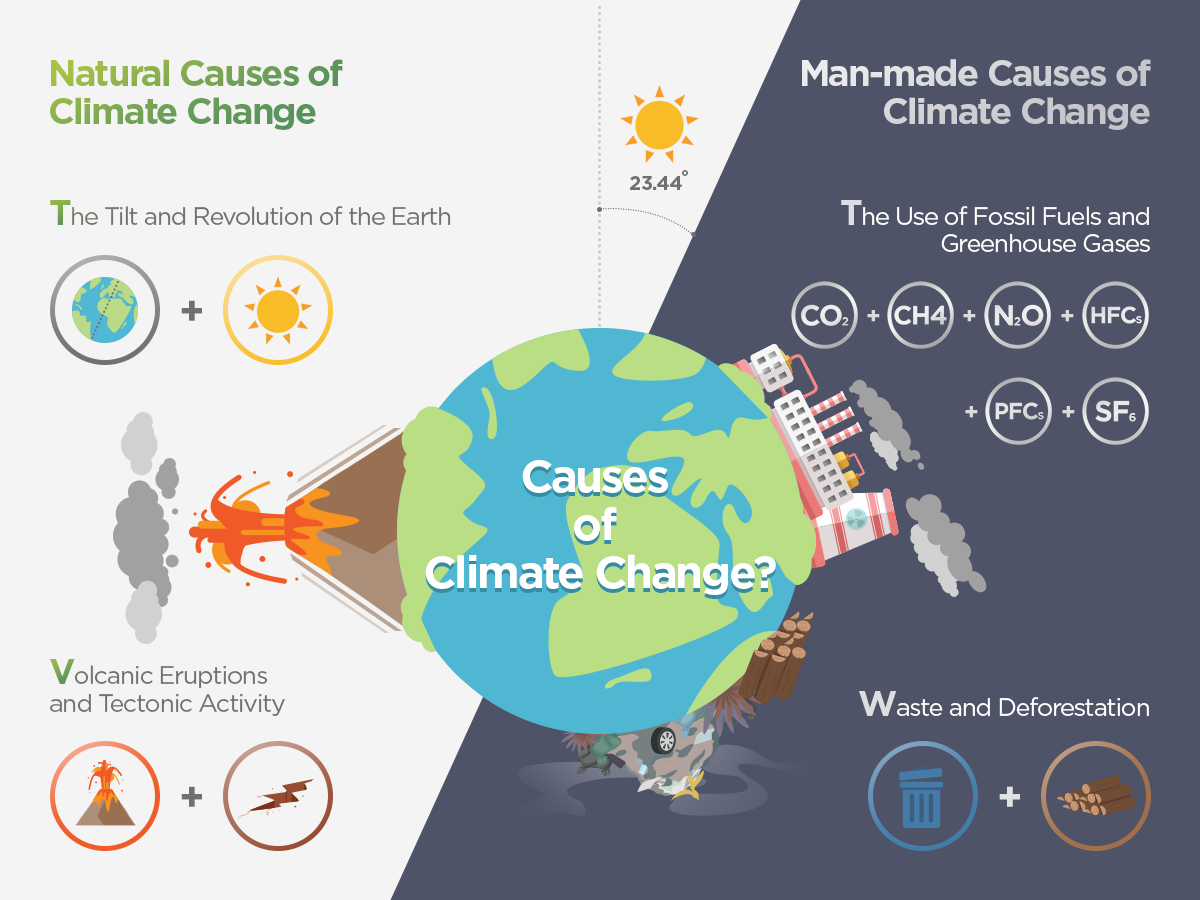 There are various contributors to the rising global temperatures
There are various contributors to the rising global temperatures
Streams of Change
But why are we seeing these record highs and lows all within the same year? The use of fossil fuels and greenhouse gases, along with improper handling of waste are major contributors caused by humankind. Volcanic activity and other natural phenomena also add to changes in climate. Along with this activity, the cause of some extreme temperature shifts can be explained with the term ‘streams.’ Jet streams are fast-flowing air currents high in the atmosphere that affect wind speeds and atmospheric pressure while being largely influential on the weather we experience on the surface of the earth.
Experience jet streams around the world with this interactive map!
The North Atlantic jet stream is influential over the weather and temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere. This wind current is located 8-12km above the surface of the earth and typically moves at around 170kph. There are a total of 4 such jet streams around the globe. The North Atlantic jet stream is responsible for keeping cool air above the North Pole, but when it strays from its normal path, it can cause extreme temperatures in certain regions. An atypical dip south is what caused the record-setting cold temperatures in Chicago and across the Mid-western United States in January. Abnormally warm air rose north from the Southern Atlantic Ocean and pushed the stream over further south over central North America. Likewise, a northern shift in the stream is responsible for the heatwave across Europe this summer.
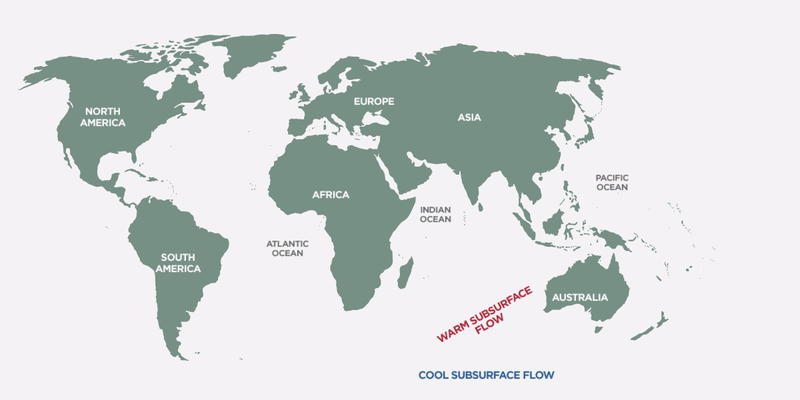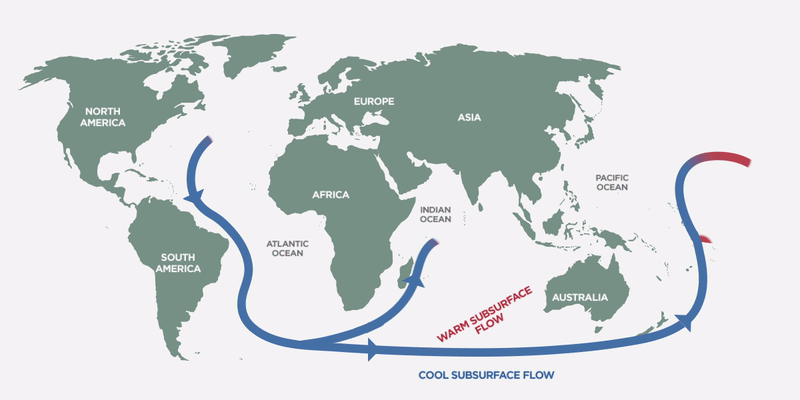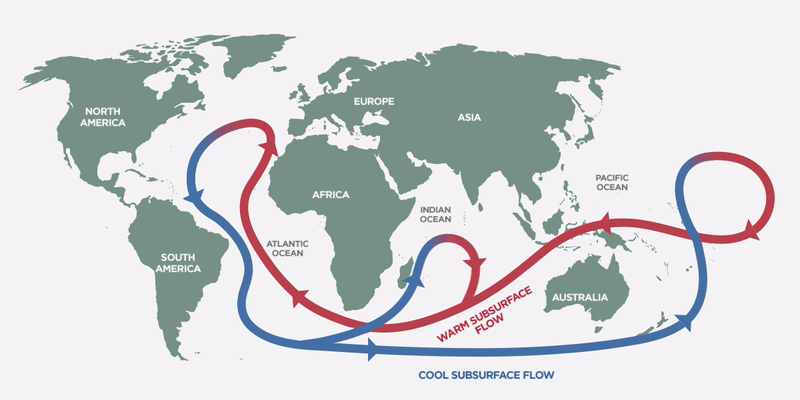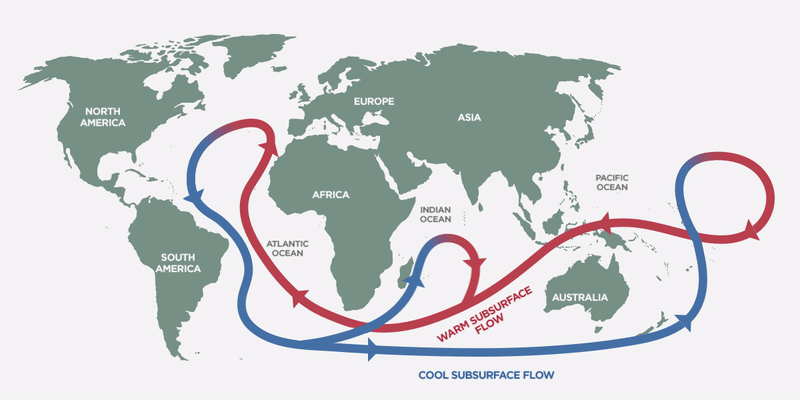 Thermohaline Circulation maintains a balance in ocean temperatures and impacts climate
Thermohaline Circulation maintains a balance in ocean temperatures and impacts climate
The well-known Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean is actually part of a global-scale ocean conveyor system known as the Thermohaline Circulation that keeps a balanced mix throughout the oceans around the world. The ocean is also in constant motion with strong currents like the Gulf Stream that affect regional climates around the world. For example, England is actually on the same parallel as some very cold regions in Canada but enjoys a much warmer weather thanks to the Gulf Stream, bringing warm water north from the Gulf of Mexico. As this warm water moves north, colder water is pushed to the bottom of the ocean and it moves south all the way down to Antarctica. That’s quite a journey!
You may have experienced some abnormal highs or lows in temperatures in your region too. The many systems that keep our planet in balance are complex and continually changing. As the global average temperature is rising, we are surely feeling the effects of these changes. We’ll see if 2020 has any more temperature records on the way.


































